User Guide

Welcome to Le Tracker ~
“The tragedy in life doesn’t lie in not reaching your goal. The tragedy lies in having no goal to reach.” - Benjamin E. Mays
School is hard. With numerous modules to juggle and endless topics to master, being a student can feel overwhelming at times. But does this truly need to be the case?
We believe that with a little help, content mastery is more than achievable.
“You don’t actually do a project; you can only do action steps related to it. When enough of the right action steps have been taken, some situation will have been created that matches your initial picture of the outcome closely enough that you can call it “done.” ― David Allen, Getting Things Done: The Art of Stress-Free Productivity
Le Tracker makes it easy to measure your overall study progress by tracking how much lecture content you have covered across various modules. More than just a simple to-do list app, Le Tracker blends the efficiency of a command line interface with the elegance of modern graphical user interface.
Now it’s time to CONQUER the semester!
Table of Contents
- Quick Start Guide
- Command Syntax
- Argument Formats
- Navigation
- Command Manual
- Notes
- Warning
- FAQ
- Command Summary
Quick Start Guide
Prerequisite
Make sure you have Java 11 installed on your computer by typing java --version from your terminal. The output should be something similar to:
openjdk 11.0.18 2023-01-17 LTS
OpenJDK Runtime Environment Zulu11.62+17-CA (build 11.0.18+10-LTS)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM Zulu11.62+17-CA (build 11.0.18+10-LTS, mixed mode)
If not, please download it from the Oracle website.
Installation and Setup
-
Download the latest version of letracker.jar.
-
Open your terminal and navigate to the directory of the downloaded jar file.
-
Run the jar file by
java -jar letracker.jar.
User Interface and Getting Started
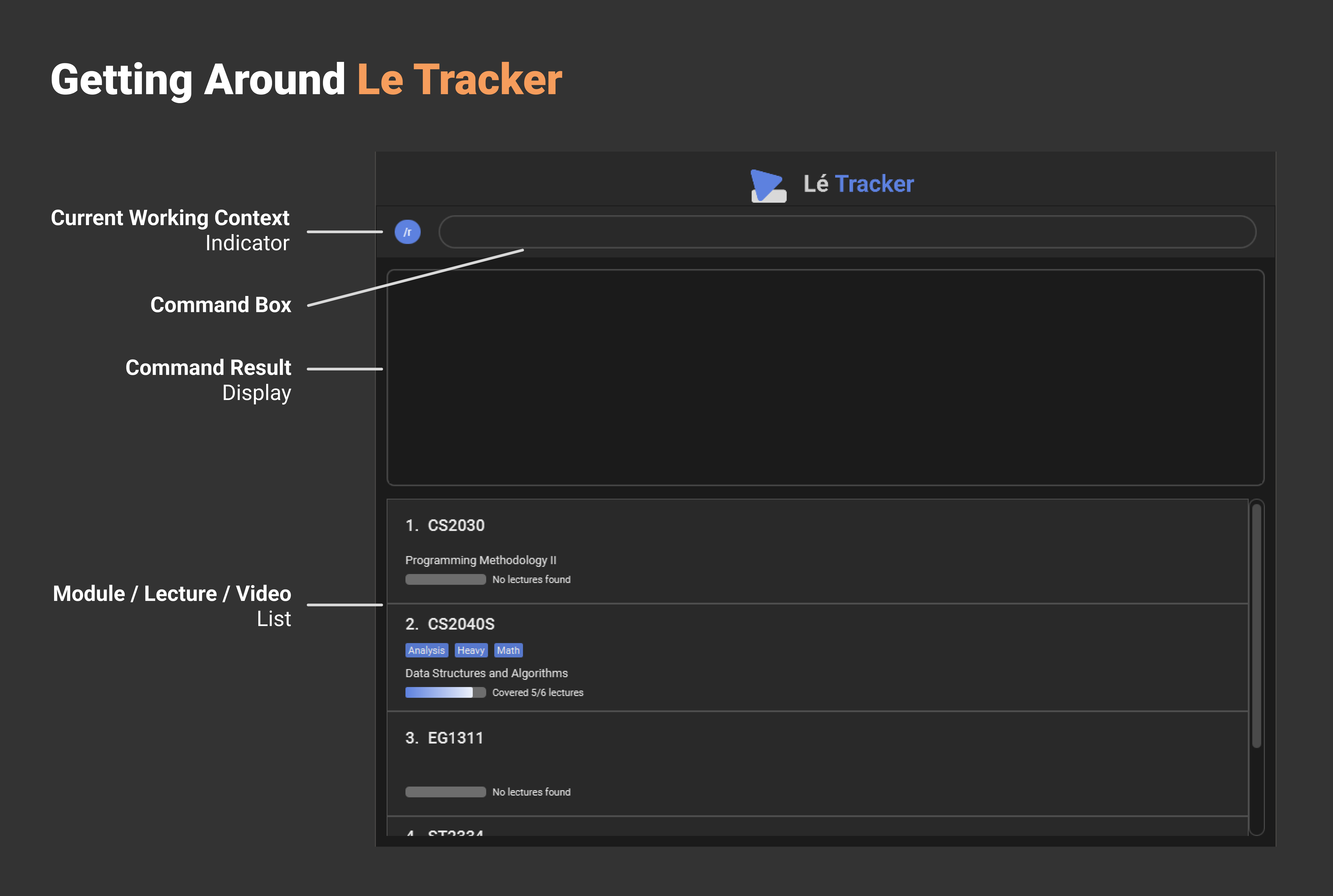
-
Type any input in the command box.
-
Press
Enterto execute a command.
For example, typinghelpand pressingEnterwill open the help window. -
Use
 and
and  arrow keys to scroll through previous commands that were executed successfully.
arrow keys to scroll through previous commands that were executed successfully.
A Brief Guide to Navigation
Current Working Context Indicator
-
The blue label on the left of the command box displays your current working context.
-
Navigating to different contexts
- Here are some ways you can navigate between different contexts.
For more information on navigation, please view the navigation section.
Tutorials and Examples
![]() Both scenarios achieve the same results, the difference lies in the context system used. You may try either one of the scenarios. If you are familiar with navigation, try out
Both scenarios achieve the same results, the difference lies in the context system used. You may try either one of the scenarios. If you are familiar with navigation, try out Scenario 2 to be more comfortable with the syntax. If not, try out Scenario 1 to gain a better understanding of how navigation works.
Scenario 1 - Using Navigation
- To add a module, execute
add CS2103 /name Software Engineering. - To add a tag of
BestModule, executetag CS2103 /tags BestModule. - To navigate into module
CS2103, executenav CS2103. - To add a lecture, execute
add Week 1. - To navigate into lecture
Week 1, executenav Week 1. - To add a video, execute
add Vid 1. - To edit a timestamp, execute
edit Vid 1 /timestamp 01:20:15. - To mark video as watched, execute
mark Vid 1. - To change video name to
video 1, executeedit Vid 1 /name video 1. - To delete a video, execute
delete video 1. - To navigate back into module
CS2103and list it’s lectures, executenavb. - To add a tag of
Intro, executeedit Week 1 /tags Intro. - To remove a tag of
Intro, executeuntag Week 1 /tags Intro. - To navigate back to root context and list all modules, execute
navornavb.
Scenario 2 - Not using Navigation
- To add a module, execute
add CS2103 /name Software Engineering. - To add a tag of
BestModule, executetag CS2103 /tags BestModule. - To add a lecture, execute
add Week 1 /mod CS2103. - To add a video, execute
add Vid 1 /mod CS2103 /lec Week 1. - To edit a timestamp, execute
edit Vid 1 /mod CS2103 /lec Week 1 /timestamp 01:20:15. - To list videos, execute
list /mod CS2103 /lec Week 1. - To mark video as watched, execute
mark Vid 1 /mod CS2103 /lec Week 1. - To change video name to
video 1, executeedit Vid 1 /mod CS2103 /lec Week 1 /name video 1. - To delete a video, execute
delete video 1 /mod CS2103 /lec Week 1. - To list lectures, execute
list /mod CS2103. - To add a tag of
Intro, executeedit Week 1 /mod CS2103 /tags Intro. - To remove a tag of
Intro, executeuntag Week 1 /mod CS2103 /tags Intro. - To list all modules, execute
list.
![]() That covers all the main commands. Refer to the Command Manual section for details of each command. Feel free to play around with the sample data to familiarise yourself with the commands. Once you are comfortable, execute
That covers all the main commands. Refer to the Command Manual section for details of each command. Feel free to play around with the sample data to familiarise yourself with the commands. Once you are comfortable, execute clear to delete all data and start from scratch.
Command Syntax
![]() Named arguments are arguments which have a prefix while unnamed arguments are arguments without a prefix.
Named arguments are arguments which have a prefix while unnamed arguments are arguments without a prefix.
e.g. For the command add CS2040S /name DSAG, “CS2040S” is the value of the unnamed argument and “DSAG” is the value of the named argument /name.
- Items in curly braces (i.e.
{}) are placeholders for some actual value. In a command format, they represent the argument values to be supplied by the user.Example
For a command with formatadd {module_code},{module_code}is an argument value. The command can be used asadd CS2040. - Items in square brackets (i.e.
[]) are optional.Example
For a command with formatadd {module_code} [/name {module_name}], the/nameargument is optional. The command can be used asadd CS2040 /name Data Structures and Algorithmsor asadd CS2040. - An ellipsis (i.e.
...) indicates that multiple values can be provided.Example
For a command with formattag {module_code} /tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, {tag_3}[, ...]]], the/tagsargument can take multiple values. The command can be used astag CS2040S /tags Heavy, Hard, Math, Analysis. - Named arguments can be specified in any order as long as it is after all unnamed arguments (if any).
Example
For a command with formatedit {module_code} /code {updated_code} /name {updated_name}, the command can be used asedit CS2040 /code CS2040S /name DSAGor asedit CS2040 /name DSAG /code CS2040S. - If a named argument is expected only once in the command but the user specified it multiple times, only the last occurrence of the argument will be taken.
Example
For a command with formatadd {module_code} [/name {module_name}], if used asadd CS2040 /name Data Structures and Algorithms /name DSAG,DSAGwill be taken as the value of the/nameargument. - Extraneous arguments will be ignored.
Example
For a command with formatadd {module_code} /name {module_name}, if used asadd CS2040 /name DSAG /foo bar, the/fooargument is ignored. - Any occurrence of
/{argument_name}, where{argument_name}contains only alphabetical characters (a-z, A-Z), will be treated as a named argument if the following 2 conditions are met:- There is a whitespace before
/{argument_name} -
/{argument_name}is followed by a whitespace or it is the end of the command
Example
For the commandfind Intro /mod CS2040S /byTag,/modand/byTagare both recognised as named arguments. For the commandfind Intro /modCS2040S /byTag, only/byTagis recognised as a named argument whileIntro /modCS2040Sis treated as the value of the unnamed argument. - There is a whitespace before
Argument Formats
-
Lecture Name
Lecture names should only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank.
e.g. Week 1 -
Module Code
Module codes should begin with uppercase alphabetical characters (A-Z), followed by numeric characters, optionally followed by more uppercase alphabetical characters (A-Z).
e.g. CS2040S -
Module Name
Module names should only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it can be blank.
e.g. Data Structures and Algorithms -
Tag
Tags should only contain alphanumeric characters, and it should not be blank.
e.g. 4MCs -
Timestamp
Timestamp should be of the format
HH:mm:sswhereHHis the number of hours,mmis the number of minutes, andssis number of seconds, each integer being exactly 2 digits long.
e.g. 01:20:03 -
Video Name
Video names should only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces, and it should not be blank.
e.g. Video 1
Navigation
Current Working Context
Le Tracker organises content using a hierarchical structure (Modules -> Lectures -> Videos). When you are studying a specific lecture topic (e.g. Week 1 of CS2040S), you may find yourself frequently performing commands that are related to the module “CS2040S” and lecture “Week 1”.
To avoid the need to constantly specify the module and lecture parameters for such commands, the navigation system allows you to specify a current working context instead.
Type of contexts
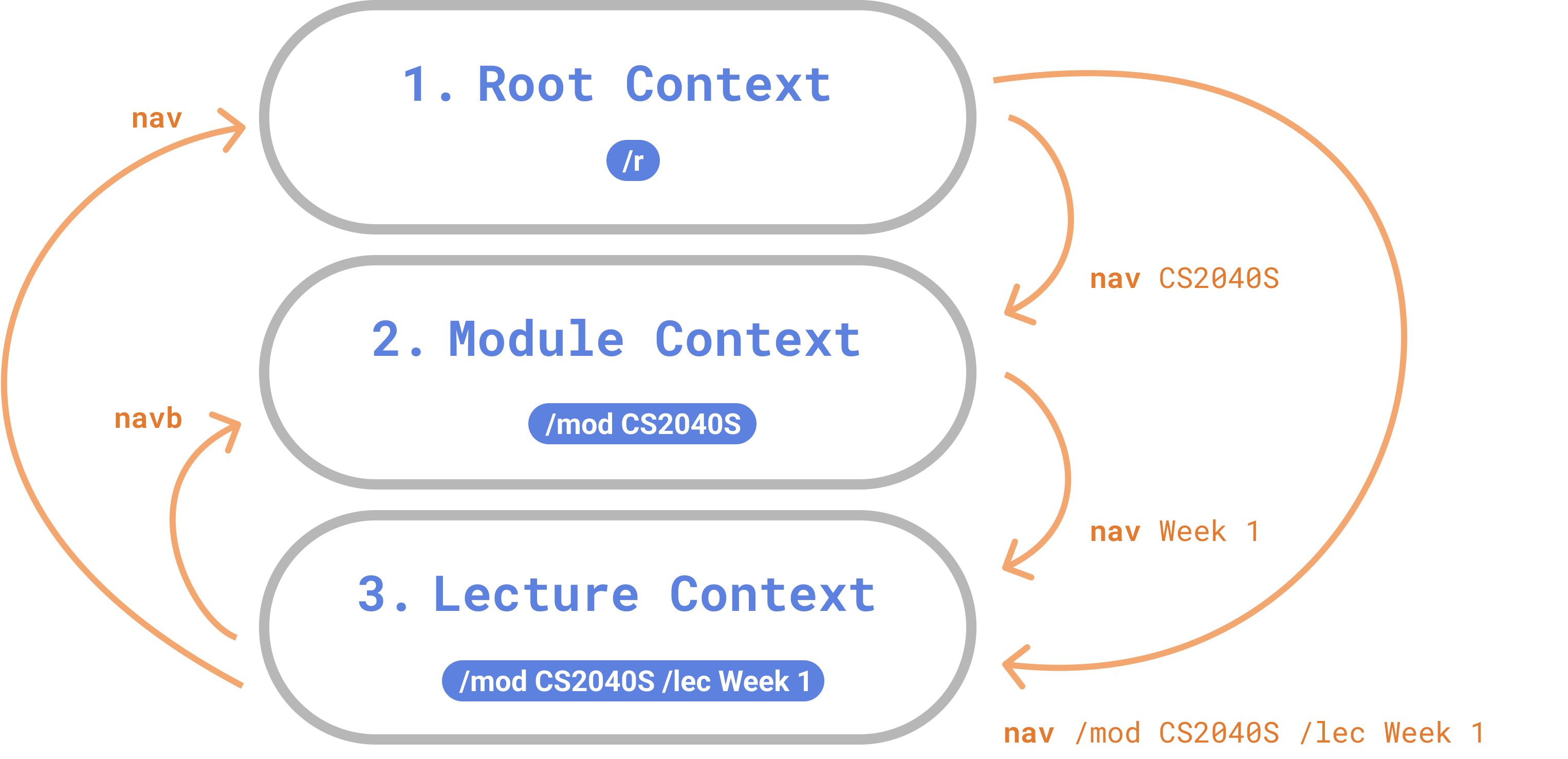
-
 Root context: The default and top-most context.
Root context: The default and top-most context. -
 Module context: Represents a specified module.
Module context: Represents a specified module. -
 Lecture context: Represents a specified lecture that belongs to a specified module.
Lecture context: Represents a specified lecture that belongs to a specified module.
Two Ways of Navigating
You can specify a current working context by navigating.
- There are two ways of navigating - relatively or directly.
For example, you can navigate to the lecture context - lecture “Week 1” of the module “CS2040S” by
-
Navigating relatively from the root context

- Navigate to the module context from the root context.
nav CS2040S - Navigate to the lecture context from the module context.
nav Week 1
- Navigate to the module context from the root context.
-
Navigating directly from any context



- Navigate directly to the lecture “Week 1” of the module “CS2040S”.
nav /mod CS2040S /lec Week 1
- Navigate directly to the lecture “Week 1” of the module “CS2040S”.
Navigation Injection
After navigating to a lecture or module context, the navigation system will inject the required module and lecture parameters (i.e. /mod CS2040S, /lec Week 1) into commands so you don’t have to!
Here are some examples of how the navigation system injects the necessary context-related parameters into your commands:
-
 Add “Video 2” to the lecture “Week 1” of module “CS2040S”.
Add “Video 2” to the lecture “Week 1” of module “CS2040S”.
add Video 2->add Video 2 /mod CS2040S /lec Week 1 -
 List the videos of lecture “Week 1” of module “CS2040S”.
List the videos of lecture “Week 1” of module “CS2040S”.
list->list /mod CS2040S /lec Week 1 -
 Add “Video 1” to lecture “Week 1” of module “CS2040S”.
Add “Video 1” to lecture “Week 1” of module “CS2040S”.
add Video 1 /lec Week 1->add Video 1 /mod CS2040S /lec Week 1
Specifying Your Own Context In Commands
To specify your own context for a command without any injection, you can use the /r, /mod, /lec arguments in your commands.
The following can be performed at any current working context
- Including the
/rargument will perform a command from the root context.- e.g. List all modules at the root context.
list /r->list
- e.g. List all modules at the root context.
- Including the
/modargument will perform a command from the module context.- e.g. Add lecture “Week 10” for module “CS2040S”.
add Week 10 /mod CS2040S->add Week 10 /mod CS2040S(No injection)
- e.g. Add lecture “Week 10” for module “CS2040S”.
- Including the
/modand/lecarguments will perform a command from the lecture context.- e.g. Add video “BST Challenge” for lecture “Week 5” of module “CS2040S”.
add BST Challenge /mod CS2040S /lec Week 5->add BST Challenge /mod CS2040S /lec Week 5(No injection)
- e.g. Add video “BST Challenge” for lecture “Week 5” of module “CS2040S”.
To make it easier to specify a lecture context which shares the same module code as your current working context, the /mod prefix can be injected when only the /lec prefix is specified.
- e.g.
 List videos of lecture “Week 5” of module “CS2040S”.
List videos of lecture “Week 5” of module “CS2040S”.
list /lec Week 5->list /mod CS2040S /lec Week 5
- Note that the lecture week is different from the current working context and that only the
/modprefix has been injected into the command input.
Command Manual
![]() The matching of values is case sensitive unless otherwise stated. For example, the lecture names “Week 1” and “week 1” are not the same.
The matching of values is case sensitive unless otherwise stated. For example, the lecture names “Week 1” and “week 1” are not the same.
![]() If an argument value requires a specific format, click the argument value placeholder beside the argument description to go to the section containing the format.
If an argument value requires a specific format, click the argument value placeholder beside the argument description to go to the section containing the format.
Nav
Navigate to the Root Context
navNavigate to the root context from any context.
Navigate from Root Context to Module Context
nav {module_code}
Navigates from the root context to a module context.
-
module_code: The code of the module to navigate to- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
Navigate from Module Context to Lecture Context
nav {lecture_name}
Navigates from a module context to a lecture context.
-
lecture_name: The name of the lecture to navigate to- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module of the current working context
Navigate Directly
nav /mod {module_code} [/lec {lecture_name}]
Navigates directly to the specified module or lecture context.
-
module_code: The code of the module that contains the lecture specified inlecture_name- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
lecture_name: The name of the lecture to navigate to- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
module_code
- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
Navigate Backwards
navb
Navigates backwards to a higher context unless already at root context.
List
![]() Items are listed in an alphabetical order sorted by
Items are listed in an alphabetical order sorted by module_code for Module, lecture_name for Lecture and video_name for Video.
List Modules
list
![]()
![]() When in a module or lecture context, the navigation system will inject the
When in a module or lecture context, the navigation system will inject the /mod and /lec arguments transforming the user’s command into the command specified in List Lectures or List Videos (refer to Navigation Injection for more information).
List Lectures
list /mod {module_code}
Lists all lectures of a module.
-
module_code: The code of the module to list the lectures from.- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
Example
-
list /mod CS2040S
lists lectures belonging to module "CS2040S"
List Videos
list /mod {module_code} /lec {lecture_name}
Lists all videos of a lecture in a module.
-
module_code: The code of the module that contains the lecture specified inlecture_name- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
lecture_name: The name of the lecture- Must belong to an existing lecture in the specified
module_code
- Must belong to an existing lecture in the specified
Example
-
list /mod CS2040 /lec Week 1
lists videos in lecture "Week 1" belonging to module "CS2040S"
Find
![]() This is a case insensitive search and matches a target that starts with the search term.
This is a case insensitive search and matches a target that starts with the search term.
E.g:
| Type | Data | Keyword | Matched |
|---|---|---|---|
| ModuleCode | [CS2040S, CS2103, ST2334, MA2001] | cs21 | [CS2103] |
| LectureName | [Week 1, Week 2, Week 3] | week | [Week 1, Week 2, Week 3] |
| VideoName | [Video 1, Video 2, Some video] | video 1, some | [Video 1, Some video] |
Find Modules
find {keywords} [/byTag]
Find all modules whose code starts with any of the keyword(s).
-
/byTag: If specified, the list filters for modules whose tag list contains any tag that starts with any of the keyword(s)
![]()
![]() When in a module or lecture context, the navigation system will inject the
When in a module or lecture context, the navigation system will inject the /mod and /lec arguments transforming the user’s command into the command specified in Find Lectures or Find Videos (refer to Navigation Injection for more information).
Example
-
Assuming only a module "CS2040S" has tags ["heavy", "math"],
find heav /byTag
will list modules ["CS2040S"].
Find Lectures
find {keywords} /mod {module_code} [/byTag]
Find all lectures in a specified module whose name starts with any of the keyword(s).
-
module_code: The code of the module that contains the lecture specified inlecture_name- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
/byTag: If specified, the list filters for lectures in a specified module whose tag list contains any tag that starts with any of the keyword(s)
Example
-
find week 1, week 2 /mod CS2040S
will list lectures ["Week 1", "Week 2"] of module "CS2040S". -
find intro, array /mod CS2040S /byTag
will list lectures belonging to module "CS2040S" with tags containing "intro" or "array".
Find Videos
find {keywords} /mod {module_code} /lec {lecture_name} [/byTag]
Find all videos in a specified lecture in a specified module whose name starts with any of the keyword(s).
-
module_code: The code of the module that contains the lecture specified inlecture_name- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
lecture_name: The name of the lecture- Must belong to an existing lecture in the specified
module_code
- Must belong to an existing lecture in the specified
-
/byTag: If specified, the list filters for videos in a specified lecture in a specified module whose tag list contains any tag that starts with any of the keyword(s)
Example
-
find vid1, vid2 /mod CS2040S /lec Week 2
will list videos ["Vid1", "Vid2"] in lecture Week 2 of module "CS2040S". -
find content /mod CS2040S /lec Week 2 /byTag
will list videos belonging to lecture "Week 2" of module "CS2040S" with tags containing "content".
Add
Add a Module
add {module_code} [/name {name}] [/tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, ...]]]
Add a module to Le Tracker.
-
module_code: The code of the module- Must be unique among the module code of the modules in Le Tracker
-
module_name: The name of the module -
tag_1, tag_2, ...: The tags to apply to the module- Repeated tags (if any) will be ignored
Example
-
add CS2040S /name Data Structures and Algorithms /tags Heavy, Math, Analysis
Add a module with code "CS2040S" to Le Tracker. The module is named "Data Structures and Algorithms" and has tags "Heavy", "Math", and "Analysis".
![]()
![]() When in a module or lecture context, the navigation system will inject the
When in a module or lecture context, the navigation system will inject the /mod and /lec arguments transforming the user’s command into the command specified in Add a Lecture or Add a Video (refer to Navigation Injection for more information).
Add a Lecture
add {lecture_name} /mod {module_code} [/tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, ...]]]
Add a lecture to a module.
-
lecture_name: The name of the lecture- Must be unique among the names of the lectures belonging to the module specified in
module_code
- Must be unique among the names of the lectures belonging to the module specified in
-
module_code: The code of the module to add the lecture to- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
tag_1, tag_2, ...: The tags to apply to the lecture- Repeated tags (if any) will be ignored
Example
-
add Week 1 /mod CS2040S /tags Intro, Important
Add a lecture named "Week 1" to the module with code "CS2040S". The lecture has tags "Intro" and "Important".
Add a Video
add {video_name} /mod {module_code} /lec {lecture_name} [/timestamp {timestamp}] [/tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, ...]]] [/watch]
Add a video to a lecture.
-
video_name: The name of the video- Must be unique among the names of the videos belonging to the lecture specified in
lecture_name
- Must be unique among the names of the videos belonging to the lecture specified in
-
module_code: The code of the module that contains the lecture specified inlecture_name- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
lecture_name: The name of the lecture to add the video to- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
module_code
- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
-
timestamp: The timestamp of the video where the user last stopped watching at- Defaults to
00:00:00if the/timestampargument is not specified
- Defaults to
-
tag_1, tag_2, ...: The tags to apply to the video- Repeated tags (if any) will be ignored
-
/watch: If specified, the video will be marked as “watched”, else, it will be marked as “not watched”
Example
-
add Video 1 /mod CS2040S /lec Week 1 /timestamp 01:04:20 /tags Intro, Short /watch
Add a video named "Video 1" to the lecture named "Week 1" which belongs to the module with code "CS2040S". The video has timestamp "01:04:20" and has tags "Intro" and "Short". The video is also marked as watched.
![]()
![]() When in a module or lecture context, the
When in a module or lecture context, the /mod argument will be injected if only the /mod argument is omitted in the original command (refer to Navigation Injection for more information).
Edit
Edit a Module
edit {module_code} [/code {updated_code}] [/name {updated_name}] [/tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, ...]]]
Edit the details of a module.
-
module_code: The code of the module to be edited- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
updated_code: The updated module code- Must be unique among the module code of the modules in Le Tracker
-
updated_name: The updated module name -
tag_1, tag_2, ...: The tags that will replace the current tags applied to the module- Repeated tags (if any) will be ignored
Example
-
edit CS2040S /code CS2040 /name DSAG /tags Heavy, Math, Analysis
Edit the module with code "CS2040S". The module's code is updated to "CS2040", it's name updated to "DSAG" and it's tags are updated to "Heavy", "Math" and "Analysis".
![]()
![]() When in a module or lecture context, the navigation system will inject the
When in a module or lecture context, the navigation system will inject the /mod and /lec arguments transforming the user’s command into the command specified in Edit a Lecture or Edit a Video (refer to Navigation Injection for more information).
Edit a Lecture
edit {lecture_name} /mod {module_code} [/name {updated_name}] [/tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, ...]]]
Edit the details of a lecture.
-
lecture_name: The name of the lecture to be edited- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
module_code
- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
-
module_code: The code of the module that contains the lecture specified inlecture_name- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
updated_name: The updated lecture name- Must be unique among the names of the lectures belonging to the module specified in
module_code
- Must be unique among the names of the lectures belonging to the module specified in
-
tag_1, tag_2, ...: The tags that will replace the current tags applied to the lecture- Repeated tags (if any) will be ignored
Example
-
edit Week 1 /mod CS2040S /name Week 01 Introduction /tags Intro, Important
Edit the lecture named "Week 1" in the module with code "CS2040S". The lecture's name is updated to "Week 01 Introduction" and it's tags are updated to "Intro" and "Important".
Edit a Video
edit {video_name} /mod {module_code} /lec {lecture_name} [/name {updated_name}] [/timestamp {updated_timestamp}] [/tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, ...]]] [/watch] [/unwatch]
Edit the details of a video.
-
video_name: The name of the video to be edited- Must belong to an existing video in the lecture specified in
lecture_name
- Must belong to an existing video in the lecture specified in
-
module_code: The code of the module that contains the lecture specified inlecture_name- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
lecture_name: The name of the lecture that contains the video specified invideo_name- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
module_code
- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
-
updated_name: The updated video name- Must be unique among the names of the videos belonging to the lecture specified in
lecture_name
- Must be unique among the names of the videos belonging to the lecture specified in
-
updated_timestamp: The updated timestamp of the video where the user last stopped watching at -
tag_1, tag_2, ...: The tags that will replace the current tags applied to the lecture- Repeated tags (if any) will be ignored
-
/watch: If specified, the video will be marked as “watched”- If this argument is specified, then
/unwatchshould not be specified
- If this argument is specified, then
-
/unwatch: If specified, the video will be marked as “not watched”- If this argument is specified, then
/watchshould not be specified
- If this argument is specified, then
Example
-
edit Video 1 /mod CS2040S /lec Week 1 /name Video 01 Grade Breakdown /timestamp 01:04:20 /tags Intro, Short /watch
Edit the video named "Video 1" in the lecture named "Week 1" which belongs to the module with code "CS2040S". The video's name is updated to "Video 01 Grade Breakdown", it's timestamp updated to "01:04:20" and it's tags are updated to "Intro" and "Short". The video is also marked as watched.
![]()
![]() When in a module or lecture context, the
When in a module or lecture context, the /mod argument will be injected if only the /mod argument is omitted in the original command (refer to Navigation Injection for more information).
Delete
Delete Module
delete {module_code_1}[, {module_code_2}[, {module_code_3}[, ...]]]
Deletes the specified module(s) and all its embodied content from the application.
-
module_code_1, module_code_2, module_code_3, ...: The codes of the modules- Must belong to existing modules in Le Tracker
- Must not contain duplicates
Examples:
-
delete CS2040
deletes "CS2040" module -
delete CS2040, ST2334
deletes "CS2040" and "ST2334" modules
![]()
![]() When in a module or lecture context, the navigation system will automatically inject the
When in a module or lecture context, the navigation system will automatically inject the /mod and /lec arguments transforming the user’s command into the command specified in Delete Lecture or Delete Video (refer to Navigation Injection for more information).
Delete Lecture
delete {lecture_name_1}[, {lecture_name_2}[, {lecture_name_3}[, ...]]] /mod {module_code}
Deletes the specified lecture(s) and all its embodied content from the same specified module.
-
lecture_name_1, lecture_name_2, lecture_name_3, ...: The names of lectures- Must belong to existing lectures in the module specified in
module_code - Must not contain duplicates
- Must belong to existing lectures in the module specified in
-
module_code: The code of module that contains the lectures specified by the names of lectures- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
Examples:
-
delete lecture 1 /mod CS2040
deletes "lecture 1" lecture found in module "CS2040" -
delete lecture 1, lecture 2 /mod ST2334
deletes "lecture 1" and "lecture 2" lectures found in module "ST2334"
Delete Video
delete {video_name_1}[, {video_name_2}[, {video_name_3}[, ...]]] /mod {module_code} /lec {lecture_name}
Deletes the specified video(s) and all its embodied content from the same specified lecture of the specified module.
-
video_name_1, video_name_2, video_name_3, ...: The names of videos- Must belong to existing videos in the lecture specified in
lecture_name - Must not contain duplicates
- Must belong to existing videos in the lecture specified in
-
module_code: The code of the module that contains the lecture specified inlecture_name- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
lecture_name: The name of the lecture that contains the videos specified by the names of videos- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
module_code
- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
Examples:
-
delete video 3 /mod CS2040 /lec lecture 1
deletes "video 3" from lecture "lecture 1" of module "CS2040" -
delete video 1, video 3 /mod CS2040 /lec lecture 1
deletes "video 1" and "video 3" from lecture "lecture 1" of module "CS2040"
![]()
![]() When in a module or lecture context, the
When in a module or lecture context, the /mod argument will be injected if only the /mod argument is omitted in the original command (refer to Navigation Injection for more information).
Mark or Unmark
mark {video_name_1}[, {video_name_2}[, {video_name_3}[, ...]]] /mod {module_code} /lec {lecture_name}
Marks video(s) as watched in lecture of its specified module.
unmark {video_name_1}[, {video_name_2}[, {video_name_3}[, ...]]] /mod {module_code} /lec {lecture_name}
Marks video(s) as unwatched in a lecture of its specified module.
-
video_name_1, video_name_2, video_name_3, ...: The names of videos- Must belong to existing videos in the lecture specified in
lecture_name - Must not contain duplicates
- For
mark, must not already be marked - For
unmarkfor 1 video, must not already be marked as unwatched
- Must belong to existing videos in the lecture specified in
-
module_code: The code of the module- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
lecture_name: The name of the lecture- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
module_code
- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
Examples:
-
mark Vid 1 /mod CS2040 /lec Week 1
marks "Vid 1" in "Week 1" lecture of "CS2040" module as watched -
mark Vid 1, Vid 2 /mod CS2040 /lec Week 1
marks "Vid 1" and "Vid 2" in lecture of "Week 1" of "CS2040" module as watched -
unmark Vid 2 /mod CS2040 /lec Week 1
marks "Vid 2" in lecture "Week 1" of module "CS2040" as unwatched -
unmark Vid 1, Vid 2 /mod CS2040 /lec Week 1
marks "Vid 1" and "Vid 2" in lecture "Week 1" of "CS2040" module as unwatched
![]()
![]() When in a module or lecture context, the
When in a module or lecture context, the /mod argument will be injected if only the /mod argument is omitted in the original command (refer to Navigation Injection for more information).
Tag
Tag a Module
tag {module_code} /tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, {tag_3}[, ...]]]
Tag a specified module.
-
module_code: The code of the module- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
tag_1, tag_2, ...: The tags to be applied to the module- Repeated tags (if any) will be ignored
- Tags that were already applied to the module (if any) will be ignored
Example:
-
tag EG2310 /tags fun, hard
Tag the module "EG2310" with the tags "fun" and "hard"
![]()
![]() When in a module or lecture context, the navigation system will inject the
When in a module or lecture context, the navigation system will inject the /mod and /lec arguments transforming the user’s command into the command specified in Tag a Lecture or Tag a Video (refer to Navigation Injection for more information).
Tag a Lecture
tag {lecture_name} /mod {module_code} /tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, {tag_3}[, ...]]]
Tag a specified lecture.
-
lecture_name: The name of the lecture- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
module_code
- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
-
module_code: The code of the module that contains the lecture specified inlecture_name- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
tag_1, tag_2, ...: The tags to be applied to the lecture- Repeated tags (if any) will be ignored
- Tags that were already applied to the lecture (if any) will be ignored
Example:
-
tag Lecture_1 /mod CS2040 /tags Yay
Tag the lecture "Lecture_1" of module "CS2040" with the tag "Yay"
Tag a Video
tag {video_name} /lec {lecture_name} /mod {module_code} /tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, {tag_3}[, ...]]]
Tag a specified video.
-
video_name: The name of the video- Must belong to an existing video in the lecture specified in
lecture_name
- Must belong to an existing video in the lecture specified in
-
lecture_name: The name of the lecture that contains the video specified invideo_name- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
module_code
- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
-
module_code: The code of the module that contains the lecture specified inlecture_name- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
tag_1, tag_2, ...: The tags to be applied to the video- Repeated tags (if any) will be ignored
- Tags that were already applied to the video (if any) will be ignored
Example:
-
tag Video_1 /lec Lecture_1 /mod CS2040 /tags Yay
Tag the video "Video_1" of lecture "Lecture_1" in module "CS2040" with the tag "Yay"
![]()
![]() When in a module or lecture context, the
When in a module or lecture context, the /mod argument will be injected if only the /mod argument is omitted in the original command (refer to Navigation Injection for more information).
Untag
Untag a Module
untag {module_code} /tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, {tag_3}[, ...]]]
Remove specified tags from a module.
-
module_code: The code of the module- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
tag_1, tag_2, ...: The tags to be removed from the module- Must belong to existing tags in the module specified by
module_code - Repeated tags (if any) will be ignored
- Must belong to existing tags in the module specified by
Example:
-
untag EG2310 /tags fun, hard
Remove the tags "fun" and "hard" from module "EG2310"
![]()
![]() When in a module or lecture context, the navigation system will inject the
When in a module or lecture context, the navigation system will inject the /mod and /lec arguments transforming the user’s command into the command specified in Untag a Lecture or Untag a Video (refer to Navigation Injection for more information).
Untag a Lecture
untag {lecture_name} /mod {module_code} /tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, {tag_3}[, ...]]]
Remove specified tags from a lecture.
-
lecture_name: The name of the lecture- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
module_code
- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
-
module_code: The code of the module that contains the lecture specified inlecture_name- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
tag_1, tag_2, ...: The tags to be removed from the lecture- Must belong to existing tags in the lecture specified in
lecture_name - Repeated tags (if any) will be ignored
- Must belong to existing tags in the lecture specified in
Example:
-
untag Lecture_1 /mod CS2040 /tags Yay
Remove the tag "Yay" from lecture "Lecture_1" of module "CS2040"
Untag a Video
untag {video_name} /lec {lecture_name} /mod {module_code} /tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, {tag_3}[, ...]]]
Remove specified tags from a video.
-
video_name: The name of the video- Must belong to an existing video in the lecture specified in
lecture_name
- Must belong to an existing video in the lecture specified in
-
lecture_name: The name of the lecture that contains the video specified invideo_name- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
module_code
- Must belong to an existing lecture in the module specified in
-
module_code: The code of the module that contains the lecture specified inlecture_name- Must belong to an existing module in Le Tracker
-
tag_1, tag_2, ...: The tags to be removed from the video- Must belong to existing tags in the video specified in
video_name - Repeated tags (if any) will be ignored
- Must belong to existing tags in the video specified in
Example:
-
untag Video_1 /lec Lecture_1 /mod CS2040 /tags Yay
Remove the tag "Yay" from video "Video_1" of lecture "Lecture_1" in module "CS2040"
![]()
![]() When in a module or lecture context, the
When in a module or lecture context, the /mod argument will be injected if only the /mod argument is omitted in the original command (refer to Navigation Injection for more information).
Export
export {file_path} [/overwrite]
Export all module data to a file.
-
file_path: The path of the file- User must have writing permission to
file_path - If
/overwriteis not specified, the file specified infile_pathmust not exist - Must be relative to Le Tracker’s default saving directory (
 The default saving directory is
The default saving directory is {JAR_file_location}/data) - Must not coincide with Le Tracker’s current tracker file path. (
 The default tracker file path is
The default tracker file path is {JAR_file_location}/data/letracker.json)
- User must have writing permission to
-
/overwrite: If specified, Le Tracker will overwrite all data infile_pathif it exists- If the file specified in
file_pathdoesn’t exist, the flag/overwritewill be ignored
- If the file specified in
Examples:
-
export hello.json
Export all modules in tracker to the filehello.jsonin the default directory -
export /../../haha.json /overwrite
Export all modules in tracker to the file path/../../haha.json, overwriting its content
Import
import {file_path} [/mod {module_code_1}[, {module_code_2}[, {module_code_3}[, ...]]]] [/overwrite]
Import data from a specified file path to the current tracker.
-
file_path: The path of the file- User must have read permission of the file in
file_path - Must be a valid Le Tracker data file
- Must be relative to Le Tracker’s default saving directory (
 The default saving directory is
The default saving directory is {JAR_file_location}/data) - The file specified in
file_pathmust exist. ( If only the file’s name is specified, the file must exist in the default saving directory at
If only the file’s name is specified, the file must exist in the default saving directory at {JAR_file_location}/data)
- User must have read permission of the file in
-
/mod: If specified, Le Tracker will only import progress from the modules specified in{module_code_1}[, {module_code_2}[, {module_code_3}[, ...]]]- If specified,
{module_code_1}[, {module_code_2}[, {module_code_3}[, ...]]]must also be specified - If unspecified, Le Tracker will import progress of all modules in the file specified in
file_path
- If specified,
-
module_code_1, module_code_2, module_code_3, ...: The modules to import fromfile_path- If
/overwriteis not specified,module_code_1, module_code_2, module_code_3, ...must not exist in the current tracker - Must belong to existing modules in the file specified in
file_path - Repeated modules (if any) will be ignored
- If
-
/overwrite: If specified, Le Tracker will overwrite existing modules progress with the progress of the imported modules, provided they have the same code- If the imported modules do not exist in the current tracker, the flag
/overwritewill be ignored
- If the imported modules do not exist in the current tracker, the flag
Examples:
-
import hello.json
Import all modules from the filehello.jsonin the default directory to the tracker -
import /../../haha.json /overwrite
Import all modules from the file path/../../haha.json, overwriting any modules that currently exists in the tracker -
import hehe.json /mod CS2040, MA2401
Import modules "CS2040" and "MA2401" from the filehehe.jsonin the default directory -
import hihi.json /mod EG2310 /overwrite
Import modules "EG2310" from the filehihi.json, overwriting the current progress of "EG2310" in the tracker
Clear
clear
Clears all data from Le Tracker.
Exit
exit
Exit the application.
Notes
-
Saving the data
Le Tracker data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually. -
Editing the data file
Le Tracker data are saved as a JSON file{JAR_file_location}/data/letracker.json. Advanced users are welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
Warning
![]() If your changes to the tracker data file makes its format invalid, Le Tracker will discard all data and start with an empty data file at the next run.
If your changes to the tracker data file makes its format invalid, Le Tracker will discard all data and start with an empty data file at the next run.
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous Le Tracker home folder.
Command Summary
| Action | Format |
|---|---|
| Navigate to the Root Context | nav |
| Navigate from Root Context to Module Context | nav {module_code} |
| Navigate from Module Context to Lecture Context | nav {lecture_name} |
| Navigate Directly | nav /mod {module_code} [/lec {lecture_name}] |
| Navigate Backwards | navb |
| List Modules | list |
| List Lectures | list /mod {module_code} |
| List Videos | list /mod {module_code} /lec {lecture_name} |
| Find Modules | find {keywords} [/byTag] |
| Find Lectures | find {keywords} /mod {module_code} [/byTag] |
| Find Videos | find {keywords} /mod {module_code} /lec {lecture_name} [/byTag] |
| Add a Module | add {module_code} [/name {name}] [/tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, ...]]] |
| Add a Lecture | add {lecture_name} /mod {module_code} [/tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, ...]]] |
| Add a Video | add {video_name} /mod {module_code} /lec {lecture_name} [/timestamp {timestamp}] [/tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, ...]]] [/watch] |
| Edit a Module | edit {module_code} [/code {updated_code}] [/name {updated_name}] [/tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, ...]]] |
| Edit a Lecture | edit {lecture_name} /mod {module_code} [/name {updated_name}] [/tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, ...]]] |
| Edit a Video | edit {video_name} /mod {module_code} /lec {lecture_name} [/name {updated_name}] [/timestamp {updated_timestamp}] [/tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, ...]]] [/watch] [/unwatch] |
| Delete Module | delete {module_code_1}[, {module_code_2}[, {module_code_3}[, ...]]] |
| Delete Lecture | delete {lecture_name_1}[, {lecture_name_2}[, {lecture_name_3}[, ...]]] /mod {module_code} |
| Delete Video | delete {video_name_1}[, {video_name_2}[, {video_name_3}[, ...]]] /mod {module_code} /lec {lecture_name} |
| Mark Video | mark {video_name_1}[, {video_name_2}[, {video_name_3}[, ...]]] /mod {module_code} /lec {lecture_name} |
| Unmark Video | unmark {video_name_1}[, {video_name_2}[, {video_name_3}[, ...]]] /mod {module_code} /lec {lecture_name} |
| Tag a Module | tag {module_code} /tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, {tag_3}[, ...]]] |
| Tag a Lecture | tag {lecture_name} /mod {module_code} /tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, {tag_3}[, ...]]] |
| Tag a Video | tag {video_name} /lec {lecture_name} /mod {module_code} /tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, {tag_3}[, ...]]] |
| Untag a Module | untag {module_code} /tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, {tag_3}[, ...]]] |
| Untag a Lecture | untag {lecture_name} /mod {module_code} /tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, {tag_3}[, ...]]] |
| Untag a Video | untag {video_name} /lec {lecture_name} /mod {module_code} /tags {tag_1}[, {tag_2}[, {tag_3}[, ...]]] |
| Export Data | export {file_path} [/overwrite] |
| Import Data | import {file_path} [/mod {module_code_1}[, {module_code_2}[, {module_code_3}[, ...]]]] [/overwrite] |
| Clear | clear |
| Exit | exit |